Chemicals from Milk
Without a doubt man's oldest manufactured food product is milk. It is almost equally certain that shortly after the first milk was collected some prehistoric experimenter found that, on standing, the liquid would first collect an oily layer on the top and ultimately would separate into a rubbery curd and a watery fluid. This fundamental observation was the basis of the dairy industry and its recently developing by-product satellite. The early dairyman soon learned to make butter from the cream layer and cheese from the curd. Utilization of the watery whey escaped him for thousands of years. Except for a few scattered successes at "whey cheese," he either threw it away or fed it to his livestock. Late in the last century the dairy chemist first learned to recover milk sugar economically from this ancient waste product, and still more recently he mastered the separation of whey proteins.
The preparation of milk for the market is today one of our largest volume processing industries. About 14 billion gallons of milk containing 15 billion pounds of solids pass through the diaries of the United States each year.
Compared to its giant parent, the diary chemicals industry is still an insignificant infant. It has, however an impressive potential for growth. Like all by-product industries its raw material is essentially a reclaimed waste. However, most "waste" materials have only limited availability. The diary chemists have a supply of about 4 billion pounds a year of milk solids on skim milk, buttermilk, and whey, which is not now used for food.
The failure to utilize this vast store of raw material cannot attributed to lack of interest on the part of the diary industry. During the last 30 years, progressive milk processors have persistently sought profitable outlets for these materials, and increasingly stringent antipollution legislation has made dispose of whey difficult in some localities, this interest has been intensified. However, the evolution had to wait on the development modern processing techniques to replace ancient, hand-operated batch type processes and reduce production costs to a reasonable level even with a waste raw material. Continuous casein-making machines, introduced in the twenties and thirties, with improvements in evaporators and drying equipment have made the milk by-product industry truly a chemical process industry and given it its present economic promise. The development of modern tank truck transportation has also contributed by making it possible to collect milk over wide areas of processing at large central plants. Transportation costs still make the collection of cheese whey from isolated plants uneconomical.
However, good products, even cheap good products, must have markets. The search for uses for pure milk proteins and carbohydrates has been both intensive and extensive. It has ranged from textile fibers to paints, to bacterial nutrients. The search has met with mixed success. In most applications the milk products must compete economically with vegetable proteins and sugars, sometimes also derived from process wastes. However, continued research, both in processes and applications, by the highly skilled teams now engaged with these problems will undoubtedly find new economic outlets for the billion pounds of milk solids still being used so inefficiently.
RAW MATERIAL
The basic raw material on which the plant operates is whole, fresh milk seldom more than a few hours from the cow. As a process raw material it has certain disadvantages. Its composition varies with the season of the year, with the feed supplied to the cow, and from cow to cow. Fortunately the intake of the Sheffield installation is sufficiently large that the latter two types of variations tend to average out. The seasonal variations largely affect the fat content of the milk which is taken out in the initial cream separation and is not involved in the chemical operation. However, seasonal irregularities, associated with the number of cows coming into production and the change to fresh feed in the spring do influence the protein and carbohydrate recovery.
Variations in the available quantity of raw material are much more critical. The milk processor, unfortunately, has little control over the manufacturer of his raw material. Cows are exceptionally docile creatures, but they cannot easily be regimented into a regular production schedule. The volume of milk supply regularly varies by a factor of 1.5 to 3, between the early winter slack and the spring flush. Effluents from processes that operate only on "flush" milk are therefore available during only part of the year. Cheese whey, which may be processed to recover lactose and whey proteins, is usually available in large volume during the late spring and summer but contracts markedly in the winter months.
Physically, milk is a combination of oil-in-water emulsion, colloidal suspension, and aqueous solution of organic and inorganic compounds. This may explain why, after undergoing intensive study, it still remains very poorly understood.
The fat is the simplest of the components to remove. Under the influence of heat, agitation, acceleration, or a combination of these agents, the emulsion is broken, and the butterfat separates out.
TABLE I. ANALYSIS OF WHOLE MILK
| |
PerCent |
| Water |
87.0 |
| Fat |
3.9 |
| Milk sugar (lactose) |
4.9 |
| Casein |
2.9 |
| Albumin |
0.6 |
| Ash |
0.7 |
| Total |
100.0 |
The colloidal particles have not proved quite so amenable to study; they are generally considered to be micelles. Estimates of their molecular weights vary widely, probably because the micelles differ in size under changing environments. The micelles contain calcium caseinate, and most evidence indicates that they also contain calcium phosphate, either in a physical complex or as a calcium phosphocaseinate.
The structure of the casein molecule itself has never been determined although at least three different types, designated alpha, beta, and gamma, have been isolated. It is one of the few proteins containing both sulfur and phosphorus, and it is known to be made up of a chain of various amino acids. However, the nature of the linkage between the amino fragments has not been decided beyond question. Casein from milk of different mammals varies slightly in composition, but fortunately Norwich needs deal only in cow's milk.
Whatever the size or composition of the protein micelles, they are easily broken up by heat, acid, alkali, or certain enzymes, notably rennin. This breaking of the micelles results in the coagulation of the casein, but it also seems to modify the molecules slightly so that there are slight differences between caseins precipitated by various media. Because of these changes precipitated casein is said to be denatured.
After the fat has been removed from the milk by the centrifuge and the casein has been precipitated, the clear, greenish liquid that remains still contains almost half the milk solids. This is the whey which is so often discarded or given away for stock feed. Lactose accounts for about 70% of the whey solids and is in solution with a small percentage of inorganic salts, mostly citrates, lactates, and phosphates. There are proteins dissolved in the whey also. These are the materials from which the whey cheese are made. They are usually lumped into two classes, albumin and globulin, although there are known to be more than two types of soluble protein present. Together they amount to about one sixth of the total protein in whole milk. Although whey proteins are commonly referred to as lactalbumin, lactoglobulins comprise the largest part of them. These lactoglobulins are very important nutritionally and may carry important antibodies.
The colostrum produced by all mammals for the first few days after they begin to lactate is high in lactoglobulin. In fact, it is the principal protein in this milk and may run as high as 8% of the total weight, whereas normal milk seldom contains more than 3.5% of total proteins. However, the law prohibits the sale of colostrum containing milk or the use of such milk in edible products.
The remainder of the whey proteins are true lactalbumins. They contain no phosphorus. Their physiological function is not fully known but they are thought to be equally as nutritious as casein. Human milk is exceptionally high in lactalbumin which may account for as much as 50% of the total protein content, but the significance of this variation is unknown. About 6% of the nitrogen in milk is contained in compounds other than casein, globulin, and albumin. This nitrogen is combined in lecithin, certain vitamins, and compounds normally found in the blood (10).
PROCESSING
Milk arrives at the Sheffield plant either in cans or stainless steel, 3000- to 4200-gallon tank trucks. Cans are unloaded directly onto a roller conveyor, checked for sweetness by smelling, and dumped into an unloading tank. The empty cans are placed in an automatic, high temperature washer which feeds them out onto the loading platform where they can be put back on the farmer's truck. The milk feeds continuously from the unloading vat, either without further cooling directly to the separators or after cooling into one off live 5000-gallon glass-lined or stainless steel, insulated holding tanks. Milk that arrives in tank trucks from outlying collection stations or other Sheffield dairies is usually pumped directly into the holding tanks. The milk is cold when it arrives, and if it is stored the temperature is kept at or below 40ºF. In accordance with Board of Health regulations.
Normally the milk is separated immediately. Before entering the cream separators, the milk is warmed to about 90ºF to agglomerate the butterfat particles and permit a more complete separation. Four standard, disk-type, solid bowl separators remove about 8 to 10% of the volume of the milk as high fat cream.
The "fat-free" milk or skim milk goes directly to a surge tank feeding the casein machine. It contains 8.5 to 8.8% solids.
CASEIN
The conditions applied in the casein machine vary with the type of product desired. Both the temperature of the precipitation and the amount of acid added have substantial effects on the structure of the curd that will be formed. The curd is larger and firmer at higher temperatures. Increasing the amount of acid makes the curd more granular and increases the solubility of the salts. Large rubbery curd is difficult to wash and tends to retain a higher salt concentration. However, fine crumbly curd produces an excessive amount of fines that must be removed from the whey or be lost in the wash water. Hence to obtain a very pure product with almost no salt content, low temperature and high acid are used along with copious washing. Where a higher salt content is not objectionable and may even be desirable, higher temperature and lower acid addition may be used. Gross variations in the skim milk to acid ratio are achieved by altering the rate of skim milk feed by changing the impeller on the skim milk transfer pump.
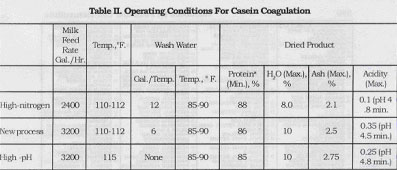
Skim milk coming to the casein machine is heated with warm water in a multiple-pass heater. Acid is added in a baffled, vertical tile cylinder. Proper addition of acid is very important to the production of uniform, high quality casein. In the Sheffield unit 37% muriatic acid is drawn from a rubberlined storage tank and diluted with water in a stoneware feed tank. From here it flows into a float controlled constant level tank through a stoneware control valve and into the acidifying chamber. The control valve is manually adjusted to produce a curd of the proper appearance and feel. The baffled cylinder ensures that all the milk comes quickly and intimately in contact with the acid so that the casein coagulum formed is of an even consistency.
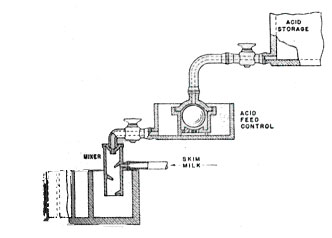
Fig 1. Acid Feed System for Casein Machine
The mixing cylinder is in one end of a stoneware box fitted with transverse baffles. In the 15 seconds it takes the curd to pass through this box, the casein precipitation is completed and the spongy mass of curd drops out on a coarse screen. A titration is run on the whey periodically to check the judgement of the operator in adjusting the acid flow. The whey that passes through the screen is caught in a tray and drained off for further processing.
The fresh curd that falls off the screen still contains about 85% water. From the screen it drops into the middle of a 30-foot ribbon conveyor inclined at 9º. This conveyor kneads and breaks the curd as it travels upward and allows the whey to drain downward to be combined with the whey from the screen drain tray. When the curd reaches the top of the draining conveyor it contains about 70% water. It drops through a curd breaker, consisting a 12-inch, troughlike sheet perforated sixth 5/8-inch holes, 1½ inches on centres. Rigid arms rotating about a central shaft at 60 r.p.m. force the curd through the perforations. When a higher purity casein is desired a second beater is installed in tandem. This supplementary breaker is 30 inches long and has 5/8-inch holes on 7/8-inch centers. Its agitator is in the shape of a square U attached at either end of the shaft which rotates 100 r.p.m. In the breaker the curd is washed with a stream of warm water. The curd at this point is about 100ºF and the wash water must be heated to avoid chilling the curd which would make it hard and cohesive. From the curd breaker the casein drops into the water-filled lower section of another conveyor identical to the draining conveyor. A spray of water plays on the top end of this converter, and as the curd is kneaded and broken and raised by the conveyer, the wash water dissolved out the occluded salts. The second conveyor discharges a curd with a moisture content of about 65% onto the squeeze rolls. Spring tension on the rolls squeezes another 15% of moisture out of the curd. At 50% moisture the curd feels almost dry and is about as dry as it can be gotten by mechanical means.
The water that drains through the screen of the squeeze rolls is caught in a pan and drained to a box with a 30-mesh screen on the bottom which separates out the casein fines. The casein fines from the whey screen and draining conveyor, also collected in this box, are settled out in a glass-lined tank (6 feet by 8 feet by 30 inches), which is drained daily and the sludge pumped to a second settling tank (44 114 24 inches). After settling, the fines from this tank are transferred into the screen-bottomed box. The filtrate water from this box is discarded. The fines are collected from the box about once a day, mixed with the oversized dried casein from the product milling separation to improve their physical characteristics, and introduced into the casein dryer.
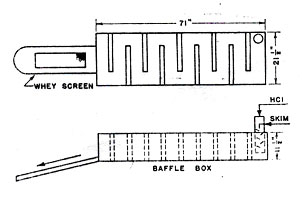
Fig 2. Baffle Box for Casein Coagulation
In spite of this procedure some fines are still lost in the wash water. These losses are greatest when high purity product is being made because this curd is less cohesive and more wash water is used.
The pressed curd from the squeeze rolls is picked up by a drag conveyor which lifts it to the spreader of conveyor dryer. The spreader is an 80-inch trough perforated with ¼-inch holes and equipped with a ribbon-type agitator revolving at 84 r.p.m. The curd at this point is quite friable and is deposited on the dryer belt in a half-inch granular layer. The drying chamber is divided into three 16-foot zones. The material passes through the unit in 30 minutes. The first zone of the dryer at 135º F is the coolest to avoid forming a hard glazed surface on the particles which would prevent further drying. Such an undesirable condition is known as case-hardening. The next two zones are at about 180º and 155ºF, respectively; heating is by steam coils.
The casein comes off the dryer conveyor with a moisture content of less than 10%. A counter-rotating screw conveyor at the end of the dryer breaks up the casein sheet and discharges to a centrifugal blower, which cools the granular product while lifting it to a cyclone separator (34 inches in diameter by 42 inches deep). From the cyclone the casein drops into a roller mill with two, nonmeshing corrugated rolls which reduce the casein to 20 to 30 inches. A screen below the mill removes oversize material which is recycled to the mill or blended with the drained fines for drying. The screen feeds directly to a bagging conveyor. All casein from the roller mill is bagged directly. That which will be further processed into hydrolyzates.
MILK PROTEIN POWDER
The product is used primarily as a supplement in human food products. When this product is to be made the wet casein from the squeeze rolls is conveyed by a drag conveyor to a hammer mill with a 0.039-inch screen. Water is introduced into the mill, and the resulting slurry (15% solids) is recycled through the mill until all the casein has been thoroughly pulverized. About 1150 pounds of wet curd (50% H2O) is fed into the mill in a batch.
Eighteen hundred gallons of skim milk are condensed to 1400 pounds of concentrate (50% solids) in a stainless steel evaporator and added to the casein slurry in a pasteurizing tank. The mixture is pasteurized at 150º F for one-half hour by a hot water jacket. It is then cooled to 120ºF and pumped to a spray dryer.
The liquid going into the dryer has a solids content of about 24%. The powdered product contains 2.5 to 3.0% moisture. The average batch produces 1200 pounds of milk protein powder which is screened through a 20-mesh screen and packed immediately in fiber drums.
CASEINATES
A small amount of casein is taken from the squeeze rolls and processed to alkali metal caseinates. To make calcium caseinate, high purity curd is milled with chilled water to very small particles. It is sometimes necessary to recycle the casein through the mill several times before the particle size is uniformly small. Calcium hydroxide does not react aggressively with casein, and if large curd particles are left in the charge they will carry through the neutralization without reacting. Chilled water must be used to hold the temperature in the mill below 60ºF. Without cooling, the friction in the mill would raise the temperature to 80ºF or higher and encourage bacterial and enzyme activity. Batch charge is 2668 pounds of wet casein and 800 gallons of chilled water.
The thin slurry is pumped to a treating tank and 40 pounds of calcium hydroxide and enough additional water to make 1220 gallons are added. After thorough mixing without heating, the pH of the batch is determined and more lime added if necessary to bring the batch to neutral pH. The neutral mixture is heated to 145ºF and held at that temperature for 1 hour with continued agitation. After this pasteurization is complete the batch is allowed to cool to 130ºF and is held at that temperature for spray drying. Other caseinates can be pasteurized at higher temperatures because they are less heat sensitive.
The 12% calcium caseinate solution is spray-dried to 2.5 to 3.0% moisture at an exhaust temperature of 180º F. The product is shifted through a 20-mesh screen and packed in fiber drums, 125 pounds to the drum. An average batch gives a yield of 1334 pounds.
Sodium and potassium caseinates are made by a similar process. A small amount of casein is extracted with methanol to remove all trace vitamins. This devitaminized casein is used primarily as a control for dietary studies.
WHEY PROTEINS
The whey that overflows from the whey settling tank, containing 6.2 to 6.4% of lactose, whey proteins, and inorganic salts is pumped into a treating tank. The next step in its processing depends on the type of whey proteins that are desired. If pure protein is desired the whey is brought to a boil by the direct introduction of steam at 125 pounds per square inch for 20 to 30 minutes. At the acidity of the untreated whey (pH 4.6) the protein begins to coagulate at about 145ºF and is almost completely precipitated at the boiling point. The precipitate contains about two thirds of the nitrogen content of the whey. The nitrogen that is not precipitated is primarily combined I nonprotein compounds. This isoelectric, coagulated lactalbumin is 75 to 80% protein and contains 5 to 7% ash. Nearly the entire production at Norwich is hydrolyzed into nutrient products at Sheffield's Oneonta plant.
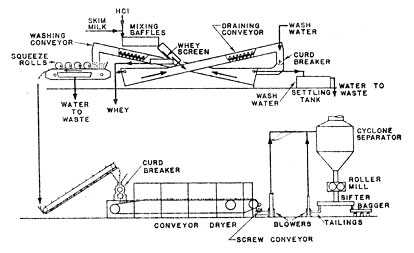
Fig 3. Sheffield Automatic Casein Machine
Most whey proteins are recovered as calcium salts by adding lime to the whey tank. The lime is made up roughly into a 10 to 20% slurry in a black iron feed tank and added to the whey until the pH is 6.8 as determined by titration. Experienced operators can estimate the proper pH of the batch from the appearance of the curd so that only a few titrations need be made. The limed whey is brought to a boil by the introduction of stem to complete the precipitation. Liming brings down about 75% of the total nitrogen in the whey. The remainder is contained in low molecular weight protein fragments, amino acids, urea, and ammoniura salts. The calcium lactalbumin precipitate is about 35 to 40% protein and contains from 35 to 40% ash. The ash constituents include most of the inorganic salts present in the original milk. However, most of these salts have dietary value, and since this material is intended for use in animal feed formulation their presence is not objectionable.
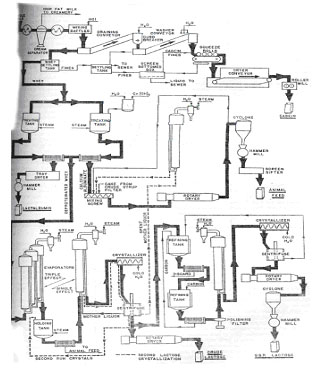
Fig 4. Flow Sheet for the Production of Milk By-Product Chemicals
After the precipitation of either isoelectric or limed lactalbumin the batch is allowed to cool and settle for 15 to 20 minutes, and the liquor is decanted off and pumped to a plate-and-frame filter press which uses diatomaceous earth as a filter-aid on duck cloths. The filtrate, a clear sugar liquor, goes to the lactose recovery unit.
The sludge from the bottom of the tank then follows the clear liquor through the filter press, the filtrate going to the lactose department. If the cake is isoelectric protein it is removed from the press and tray-dried to about 5% moisture content in a tunnel dryer. The dryer is held at 165ºF and requires 12 to 14 hours to bring the product to the desired dryness. The dried product is hammer-milled using a 0.038 screen and bagged immediately for sale or shipment to the hydrolyzate plant.
When calcium lactalbuminate is made the filter cakes is fed to a mixing screw conveyor where it is joined by exhausted mother liquor and wash waters from the sugar crystallizers which have been concentrated to 60 to 65% solids in a stainless steel evaporator. The resulting slurry is too fluid for treatment in a rotatory dryer and is mixed with five to six times its weight of recycled, dried product. The mixer discharges into a inlet of a concurrent type rotary dryer. The air to the dryer is heated by direct contact with the heating oil flame so that the stack gases also pass through the cylinder. The dryer cylinder is amply fitted with lifting baffles so that the powder is repeatedly dropped through the hot gases. The gases enter the horizontal cylinder at about 700ºF and are exhausted at about 200ºF.
The dried product is about 25% lactose, 33% protein salt, and as much as 30% ash; moisture is 5%, and inerts, primarily filteraid, 4%. The dried product is sized in a hammer mill using a 0.038-inch screen.
Exhaust gases from the dryer pass through a rotary classifier which returns entrained solids to the product line and discharges the gases to the atmosphere.
A gyratory sifter separates the sugar-protein-milk salt feed mixture into coarse and regular grades for packing in paper bags.
MILK SUGAR
The filtered, deproteinated whey from the albumin precipitating tank goes to the milk sugar operation. The first step in the treating of the liquor is to concentrate it to about 40% solids in a stainless steel, triple-effect evaporator.
The crude sirup from the evaporators is placed in one of two 8000-gallon (8159 feet) stainless steel, holding tanks. The sirup is allowed to stand overnight and then is heated by direct steam injection prior to filtration through a resin covered filter press using a diatomaceous earth precoat on duck filter cloth.
The filtrate is further concentrated to about 60% solids in a single-effect, finishing evaporator, identical to the individual effects of the primary evaporator.
The resulting thick sirup is pumped to jacketed crystallizers where cooling water reduces the temperature to 50º to 55ºF. This treatment precipitates better than 60% of the lactose in very small crystals.
At the end of the crystallizing period the slurry of sirup and crystals is dropped by gravity from the crystallizers into a perforated-basket type centrifuge. The centrifuge reduces the moisture content of the crystals to 7 to 10%. Nozzles inside the centrifuge basket wash the lactose crystals continuously with clear water. The operator watches the effluent from the centrifuge through a look box and continues the operation until the wash water runs white and clear. The quantity of wash water used with any specific batch of crystals will vary depending on the nature of the whey being processed and to a lesser extent on the conditions of crystallization. Casein whey from fresh milk usually produces relatively large, well-formed sugar crystals that wash with minimum effort. Wheys, soured by fermentation, often produce small, sticky crystals which are very difficult to wash free of mother liquor. An average batch requires 1.5 to 2.0 pounds of wash water per pound of sugar crystals.
The mother liquor and wash water from the first crystallization are returned to the single-effect evaporator where the solids content is raised back to 65% and then returned to the crystallizers. Crystallization of the second run crystals follows a cycle similar to that of the first run product. The wash water from the centrifuge in this step contains about 24% solids but only 7% lactose. This wash water is combined with the spent mother liquor to give a sirup containing about 30% solids which is sent to the feed supplement operation where it is combined with calcium lactalbuminate and dried.
Less than one quarter as much crude lactose is obtained from the second crystallizations from the first. The crystals are higher in ash and protein and are not suitable for a commercial product. Protein content may be as high as 4% which gives the crystals a dark color, and ash, mostly calcium phosphate with some calcium lactate, may run up to 10%. Furthermore, the crystals are tacky and almost impossible to dry in conventional equipment. Actually almost all these calcium salts could be removed in the pre-evaporator heating by raising the pH at that point, but such treatment would produce a darker colored sirup and make the ultimate decolorizing of the lactose more difficult. The second run crystals are utilized by recycling them to the thin sirup holding tanks. In the two crystallizations about 65% of the total lactose present is recovered. The remaining 35% ends up in the feed supplement.
The crude crystals from the first crystallization may be dried directly to produce "crude lactose". In this case the wet crystals from the centrifuge are dropped through the bottom of the basket directly to a 16-foot concurrent rotary dryer. The crystals coming out of the dryer are conveyed directly to a feed hopper which serves a simple bagging device. No milling is necessary because the product is in the form of small crystals most of which are less than 60-mesh size.
Refined Lactose. If high purity lactose is desired the crude crystals must be recrystallized. At Norwhich refined lactose is made by redissolving the crude crystals in mother liquor from the refined lactose crystallization to give a solution with a solids content of 30 to 40% (15º to 20ºBe). The solution is made in a 1850-gallon, glass-lined tank, equipped with a steam jacket. A 24-inch impeller mounted 12 inches off-center and revolving at 90 r.p.m. provides agitation in this tank. All equipment in the refined product operation from this point on is made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant material.
The lactose sirup is given a two-stage, countercurrent treatment with activated carbon. Carbon is added to a second stainless steel tank identical with the dissolving tank. This is the finishing stage of the carbon treatment. Carbon that has been used for one batch in this stage is recovered in a resin-coated plate-and-frame filter using a diatomaceous earth precoat on duck cloths and added to the dissolving tank for the initial clarification. Carbon from the dissolving tank is filtered out and discarded.
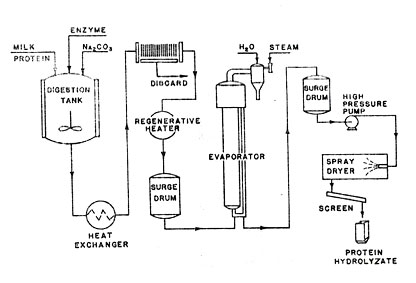
Fig 5. Production of Protein Hydrolyzates
The filtered sirup from the second stage of the carbon treatment is polished through padded filter paper backed by an asbestos mat in a single diaphragm-type filter. The filtrate from this treatment is bright clear with a slight yellow cast. The clarified sirup is concentrated to about 65 to 70% solids (30° to 35º Be) in a stainless steel single-effect evaporator of the same design as the finishing evaporator used in the crude sugar operations.
The recrystallizing procedure follows the same cycle that was used in the initial crystallization, but the crystallizers for the refined sugar are shorter and deeper than the crude crystallizers and are constructed of stainless steel.
The centrifuging and washing procedures are also the same for the refined crystals, although less wash water (1.0 to 1.5 pounds per pound of sugar) is required. The liquor and wash water from the centrifuging of the refined sugar is used to dissolve the crude so that the uncrystallized sugar is not lost. However, ash constituents build up in this recycled solvent so that at regular intervals the effluent is recycled to the deproteinized whey coming to the sugar department, and fresh water is introduced into the refined sugar operation.
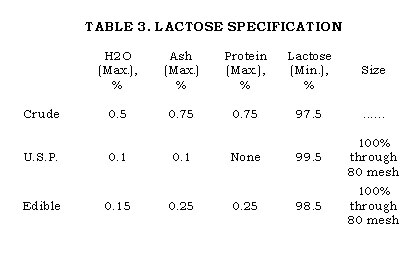
The refined lactose is U.S.P. quality with more than 99.5% sugar. It is often as much as 99.9% pure. The impurities are largely ash constituents. It is then dried in the rotary dryer at 140°F. outlet temperature. From the dryer it is picked up by a blower and carried to a mill for sizing. Classification is accomplished in a gyratory sifter. Pure lactose is used largely in food and drug preparations where the size is important for appearance and texture. The finest grade is labeled U.S.P. Impalpable and is 100% through 120 mesh and about 85% through 200 mesh. Most tablet manufacturers prefer the U.S.P. grade, which is 100% through 80 mesh. A coarser grade is usually used by food product formulators.
CASEIN HYDROLYZATES
Before beginning a batch of hydrolyzates all process equipment must be steam sterilized to destroy any residual bacteria or active enzymes that might induce fermentation or destructive hydrolysis. As a result of these precautions the hydrolyzate products contain less than 10,000 organisms per gram. However, since no hydrolyzates for parenteral injection are produced it is not necessary to keep the equipment free of pyrogens.
When casein hydrolyzates are to be made, new process casein is used as a raw material. Since Oneonta does not make casein it is drawn from Norwich or any one of three other casein plants and trucked to Oneonta is 80-pound paper bags. The casein is charged to an agitated digestion tank and slurried with 100° to 120°F water. The usual casein charge is about 5000 pounds. Ten large 5000-gallon glass-lined, digesters are available as well as two similar 2500-gallon vessels for smaller batches. The casein slurry is held at temperature by circulating controlled temperature water in the jacket.
An alkali slurry is prepared in a stainless steel make-up tank and added to the digester to solubilize the protein. Several alkalies may be used including soda ash, caustic soda, caustic potash, or ammonia depending on the product being made. Sufficient alkali is added to make the medium slightly alkaline. This brings about complete solution of the protein and near optimum conditions for the activity of the proteolytic enzymes. As the digestion proceeds the pH drops to about 6.8. Most of this drop occurs in the first 12 hours.
After the alkali slurry has been added to the digester the temperature of the charge is raised to 165°F by the water-jacket and held for at least 1 hour. Heat treatment serves to control bacterial growth and destroys undesirable enzymes and bacteria so that only the desired type of hydrolysis will occur in the digestion.
Lactalbumin hydrolzates are made by the same procedure as the casein products. The only process difference is in the temperature of the heat treatment. These are pasteurized at a higher temperature because they are more difficult to disperse, and consequently it is more difficult to ensure destruction of bacteria in the protein.
During the heat treatment a proteolytic enzyme slurry is prepared in a stainless steel make-up tank. The composition of this slurry is not measured. It is simply made up to an easily handled consistency. Any one of several enzymes can be used depending on the product desired. Trypsin, papain, pancreas gland, or fungal or bacterial enzymes can be used. The proportion of enzyme used will vary with the degree of hydrolysis desired. Chloroform and toluene are added to the enzyme mixture to inhibit bacterial growth.
The type of splitting that occurs with any given proteolytic enzyme is not too well understood. It is possible to follow the degree of splitting by measuring liberated amino nitrogen but not readily possible to follow the type or quality of splitting that occurs.
For oral use, where a source of mixed amino acids is desired, the amino nitrogen comprises at least 50% of the total nitrogen in the hydrolyzate. For bacterial nutrients the amount of splitting is variable. A range of amino nitrogen to total nitrogen of 15 to 80% may be in order.
At the end of the hour of heat treatment the charge is cooled to the digestion temperature (100° to 120°F) and the enzyme slurry is introduced. The digester is then sealed with a rubber-gasketed cover and the digestion begins. Top-entering, horizontal stirrers rotating at 12 r.p.m. provide agitation throughout the process on the large digesters. The smaller vessels have side-entering, propeller agitators. The digestion takes place at a fixed temperature maintained by the water-jacket. The digestion temperature depends on the type of enzyme used and type of protein being digested. The digestion time is determined by the degree of digestion desired, the enzyme concentration, protein concentration, temperature, and pH. Each product or variation in type of product requires a different set of digestion conditions. According to chemical analysis most of the digestion of casein is completed after 48 hours. Additional time may be required to facilitate filtration and decolorizing.
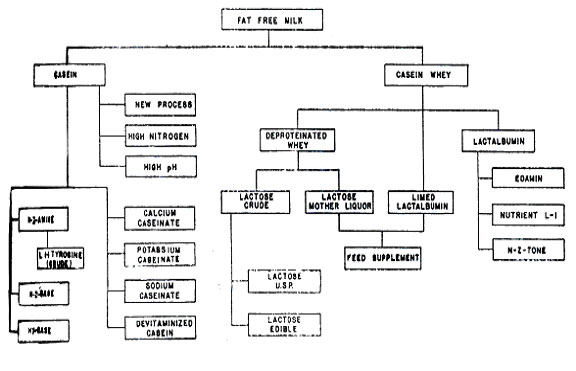
Fig 6. Chamicals from Milk
At the end of digestion the tank is opened and adsorbents or clarifying agents are added equal to about 1% of the weight of the casein charge. The hydrolyzate is pumped through a single-pass tubular heat exchanger at 170° to 180°F to solubilize the amino acids, then through a plate-and-frame filter press at about 12 gallons per minute, and finally through a plate-type heater for flash pasteurization. The cake resulting from this filtration contains about 10% of the solids charged to the digester. These solids are insoluble amino acids and insoluble enzyme residues.
TYROSIN PRODUCTION
Pure tyrosin, one of the amino acids, may be recovered from the hydrolysis liquor. In this recovery process the freshly digested liquor passes through a stainless steel settling tank equipped with bottom weirs. The tyrosin crystals settle out, and the liquor is returned to another digester and processed by the usual procedure. After the liquor has been drawn off, the tyrosin crystals are washed with water to remove residual hydrolyzates. After draining they are tray-dried at 150°F with 27 inches of mercury vacuum.
Recovery of the solid hydrolyzates from the digest is accomplished by concentrating the solution to 55 to 60% solids in a small, single-effect evaporator, operating at 135° to 140°F and then spray-drying the heavy solution. The spray dryer is a stainless steel, horizontal type and atomizes the stream at 2500 pounds per square inch gage. It has an efficient multiple cyclone dust collecting system, which permits easy cleaning and rapid change-over from one type of product to another. The hydrolyzates are light cream-colored, granular materials containing 2 to 4% moisture. They pass 100% through 140 mesh and are packaged in fiber drums without milling.
Most enzyme hydrolyzates made by Sheffield are produced by this process. The time cycle is essentially the same in all cases although the solids content of the digestion mixture may vary, and the amount of enzyme added is adjusted to control the degree of hydrolysis of the finished product. Both trypsin and pancreas are used to hydrolyze casein. Casein is also hydrolyzed with hydrochloric acid to produce Hy-Case, a food flavoring agent.
PACKAGING
The products of the Norwich plant are shipped in multiply moisture barrier bags or fiber drums, with and without polyethylene liners.
The protein hydrolyzates produced at Oneonta present a more complex problem because of their extremely hygroscopic nature. At present all these products are packed in 41-gallon fiber drums with an asphalt moisture barrier. However, a newly developed type of Hy-Case is even more sensitive to moisture than the previous products, and it necessitates the additional use of polyethylene liners in the drums.
MATERIALS OF CONSTRUCTION
Several persistent, if not acute, corrosion problems are encountered in milk by-product recovery. The milk whey itself is mildly corrosive because of the ever-present slight concentration of lactic acid. In addition corrosion problems are intensified by the addition of hydrochloric acid in processing casein and the accumulation of salts during the processing of lactose. Wherever possible, stainless steel is being substituted for copper and ordinary steel construction. Pump corrosion in the transfer of lime slurries is avoided by using steam eductor lifts for this purpose.
In the sugar plant the problem is more one of preventing contamination of the product than protecting the equipment. The evaporators are made of Type 304 stainless steel throughout, and all equipment and piping used in the production of the refined sugar is of the same material.
The plates and frames of the filters in the sugar plant are coated with a baked phenolic resin sprayed on in multiple layers over a freshly sandblasted surface. This equipment has given good service. The frames are invariably the first to fail, but they last on average of 4 years without recoating.
The centrifuge bowls for the crude sugar recovery are of bronze, but the refined sugar centrifuge is of stainless. The lines in refined sugar operation which must carry slurries containing carbon are of rubber-lined pipe. These slurries are moved by Duriron pumps. Glass pipe is used for the transportation of hydrochloric acid to the casein machine.
Solutions of protein hydrolyzates are particularly corrosive. As one operating man put it they turn a welded joint into a sponge in no time. Consequently the Oneonta plant is constructed of weldless stainless steel pipe and fittings and glass-lined and stainless steel vessels.